Unlock Authentication in .NET: JWT, Bearer Tokens & Identity Server

Authentication is the cornerstone of secure applications. Whether you're building APIs, Blazor apps, or microservices, understanding JWT tokens, Bearer authentication, and Identity Servers is essential.
In this 5-minute guide, we'll break down these concepts and show you how to implement them in .NET 10.
🔐 What is a JWT Token?
A JWT (JSON Web Token) is a compact, self-contained token that securely transmits information between parties as a JSON object. It's digitally signed, so you can trust its contents haven't been tampered with.
JWT Structure
A JWT consists of three parts separated by dots:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0In0.signature
└──── Header ──────┘└─── Payload ───────┘└─ Sig ─┘
- Header — Algorithm & token type (
alg,typ) - Payload — Claims (user data, expiration, issuer)
- Signature — Verifies the token hasn't been tampered with
Common JWT Claims
iss(Issuer) — Who created the tokensub(Subject) — The user identifieraud(Audience) — Intended recipientexp(Expiration) — When the token expiresiat(Issued At) — When the token was created
🎫 What is a Bearer Token?
A Bearer Token is a type of access token included in HTTP requests using the Authorization header:
Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9...
The term "bearer" means: "whoever bears (carries) this token is authorized."
💡 Key insight: JWTs are commonly used as bearer tokens, but they're not the same thing. JWT is a format, while Bearer is a transport mechanism.
🏢 What is an Identity Server?
An Identity Server (also called a Secure Token Service or STS) is a centralized authentication service that:
- ✅ Authenticates users (login with credentials)
- ✅ Issues tokens (JWT/access tokens)
- ✅ Validates tokens for APIs
- ✅ Supports standards like OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC)
Popular Identity Servers
- Duende IdentityServer — .NET-based, self-hosted
- Microsoft Entra ID — Azure's cloud identity (formerly Azure AD)
- Auth0 — Cloud-based, easy integration
- Keycloak — Open-source, Java-based
🔄 How It Works: The Authentication Flow
Here's how the complete authentication flow works:
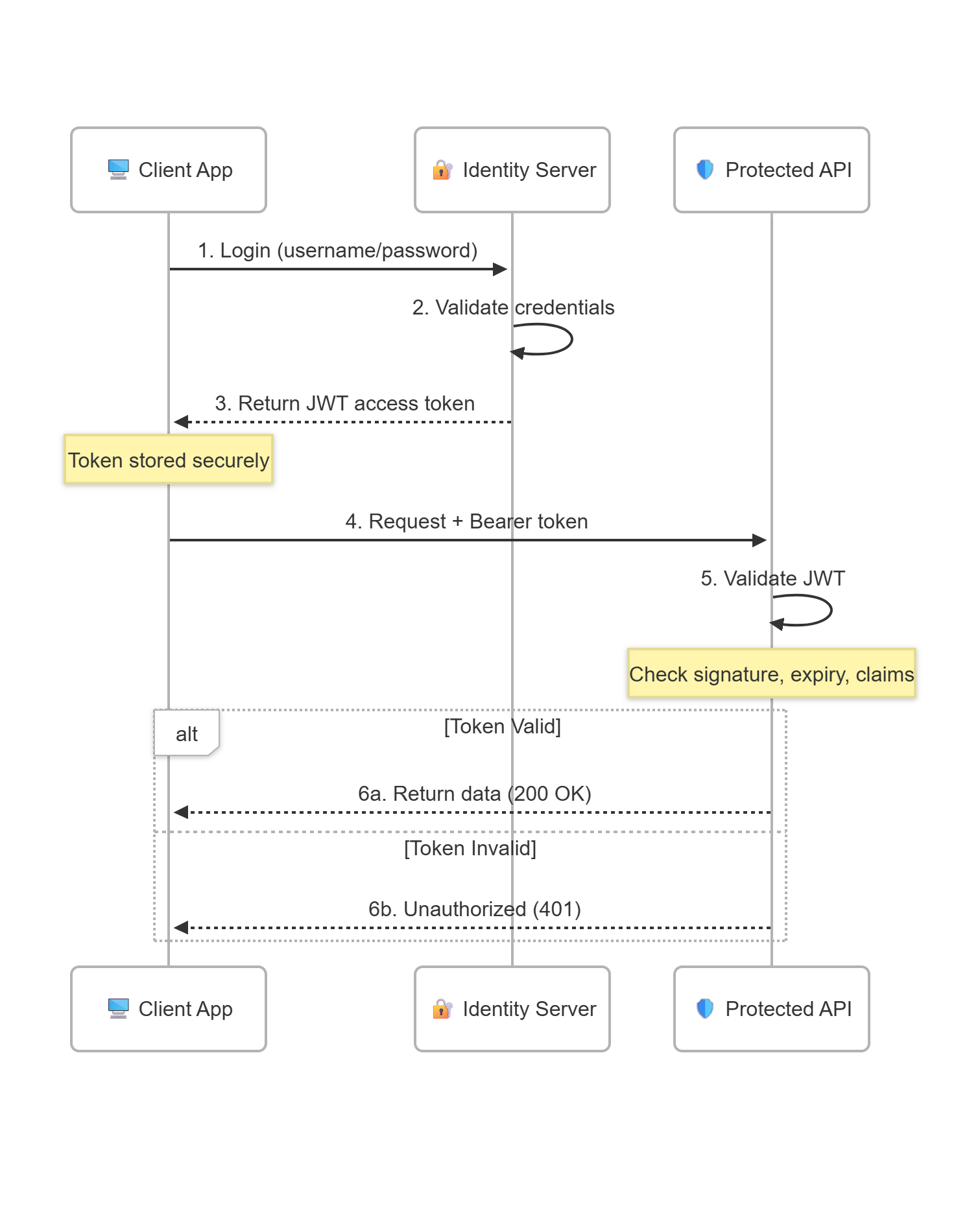
Validation Steps
When the API receives a request, it validates:
- Signature — Was this token created by a trusted issuer?
- Expiration — Is the token still valid?
- Issuer (
iss) — Did the expected identity server issue this? - Audience (
aud) — Is this token intended for this API?
💻 Implementation in .NET 10
Let's implement JWT Bearer authentication in a .NET 10 application.
Step 1: Install the NuGet Package
dotnet add package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer
Step 2: Configure JWT Authentication
// Program.cs using System.Security.Claims; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer; var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args); // Add JWT Bearer authentication builder.Services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme) .AddJwtBearer(options => { options.Authority = "https://your-identity-server.com"; options.Audience = "your-api-audience"; }); builder.Services.AddAuthorization(); var app = builder.Build(); // Enable authentication & authorization middleware app.UseAuthentication(); app.UseAuthorization(); // Public endpoint - no auth required app.MapGet("/", () => "Hello, World!"); // Protected endpoint - requires valid JWT app.MapGet("/secret", (ClaimsPrincipal user) => $"Hello, {user.Identity?.Name}! This is secret data.") .RequireAuthorization(); app.Run();
Step 3: Protect Controllers (Alternative Approach)
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; [Authorize] [ApiController] [Route("api/[controller]")] public class WeatherController : ControllerBase { [HttpGet] public IActionResult GetForecast() { return Ok(new { Temperature = 22, Unit = "Celsius" }); } [AllowAnonymous] [HttpGet("public")] public IActionResult GetPublicData() { return Ok("This is public data"); } }
Step 4: Force Authentication Globally (Optional)
If you want all endpoints to require authentication by default:
var requireAuthPolicy = new AuthorizationPolicyBuilder() .RequireAuthenticatedUser() .Build(); builder.Services.AddAuthorizationBuilder() .SetFallbackPolicy(requireAuthPolicy);
🔑 Understanding HTTP Response Codes
- 200 OK — Success: Valid token, authorized
- 401 Unauthorized — Authentication failed: Invalid/expired token, wrong signature
- 403 Forbidden — Authorization failed: Valid token, but insufficient permissions
⚡ Quick Reference
- JWT — Self-contained token with encoded claims
- Bearer Token — Token sent in
Authorizationheader - Identity Server — Issues and validates tokens (OAuth/OIDC)
- Access Token — Short-lived token for API access
- Refresh Token — Long-lived token to get new access tokens
🛡️ Security Best Practices
- Always use HTTPS — Never transmit tokens over unencrypted connections
- Validate all claims — Issuer, audience, and expiration at minimum
- Use short expiration times — Access tokens should expire in minutes, not days
- Store tokens securely — Use HTTP-only cookies for web apps, secure storage for mobile
- Use asymmetric keys — RSA or ECDSA signatures are more secure than symmetric keys
📚 Further Reading
- Configure JWT Bearer Authentication - Microsoft Docs
- OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect
- ASP.NET Core Security Documentation
See you next time for more on www.devskillsunlock.com 🚀

